SAP Cash Application using Machine Learning
SAP Cash Application using Machine Learning
Machine learning helps finance and risk teams increase automation and handle exceptions,
streamlining business processes and reducing manual errors. As opposed to rules configured in
tables — which are often never revisited, even when the business environment changes —
machine learning means just that: the system learns how to handle exceptions based on historical transactions as well as on any human, manual actions taken to deal with exceptions in the past.
Machine learning applications in SAP Cash Application
SAP Cash Application streamlines the clearing process of open items for accounts receivable (A/R) transactions. When new transactions come into the system that result in exceptions, the machine learning application takes that prior information and decides on the course of action, such as a proposal for review or an automatic clearing posting.
To begin, let’s look at A/R and the importance of SAP Cash Application.
SAP Cash Application as Part of the A/R Process
The traditional process of A/R spans several steps, as shown in Figure 1. As a contract or sales
order is created, there is a credit check against the customer, but there is no impact to general
ledger accounts in the Universal Journal. Once approved, normal logistics processes take place to fulfill the sales order, whether the manufacturing or assembly of a customized product or the sale of a product already in stock. Once the product is shipped, resulting in a financial posting against the cost of goods sold (COGS) account, the A/R process then creates an invoice, which is considered in working capital and cash flow analyses. Payment is made by the customer, which may or may not include collections and dispute activities. Once payment has been received, it is posted in A/R and cleared against the invoiced amount.

Figure 1: Traditional A/R process
The clearing of the open A/R line items is based on rules that have been configured within SAP
S/4HANA Finance, including payment terms and tolerance levels to ignore minor differences.
However, there may be many situations in which there is no one-to-one match, within the specific tolerance level, between the invoiced amount and the payment received from the customer. This could be for several reasons: the information provided with the payment may be incomplete, a reference number to the order may be missing, payment advice documentation is not legible, or duplicate master data records for the customer may exist. Alternately, there may be discrepancies in the amount paid. For example, the customer may have paid for more than one invoice in one payment, the payment received is a partial payment, there may be discrepancies based on currency conversions, or the customer may have taken an unallowed discount or paid without taking advantage of an available discount. In these and other situations, the clearing process is not straightforward, and the finance or shared services teams responsible for A/R will need to reconcile these exceptions manually. In some cases, this means reaching out to the customer.
The standard clearing process is based on the rules in configuration tables in SAP S/4HANA
Finance. To reduce the number of exceptions, SAP Cash Application was developed as a next step that includes machine learning to clear as many of these remaining open items as possible.
As shown in Figure 2, SAP Cash Application is able to act on a variety of inputs to the machine learning algorithm to clear open A/R items.
SAP Cash Application
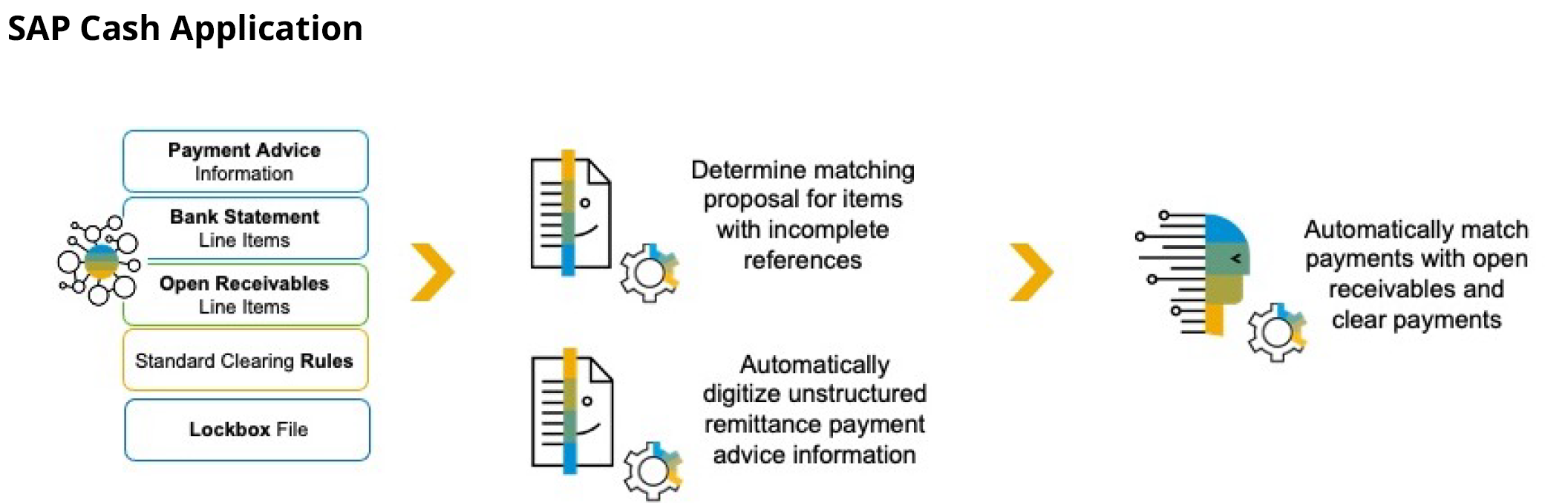
Figure 2: SAP Cash Application uses machine learning to clear A/R items that were not able to be cleared through the standard configured rules
Line items for clearing can come into SAP S/4HANA Finance in multiple ways, including open
receivable line items resulting from the sales order process, which may be entered manually, or
records imported from a bank statements file or a lockbox file. In addition, the processing of
unstructured data for payment advice information is also incorporated by SAP Cash Application, as shown in Figure 3. The format could be a PDF, a scanned document, an image, or an email. In
these situations, optical character recognition (OCR) is used to read the input documents and
extract the key information to populate transactions in the system. If the unstructured data is an audio file, such as a voicemail, it can also be transcribed using natural language processing and then used as input.
Payment Advice Extraction
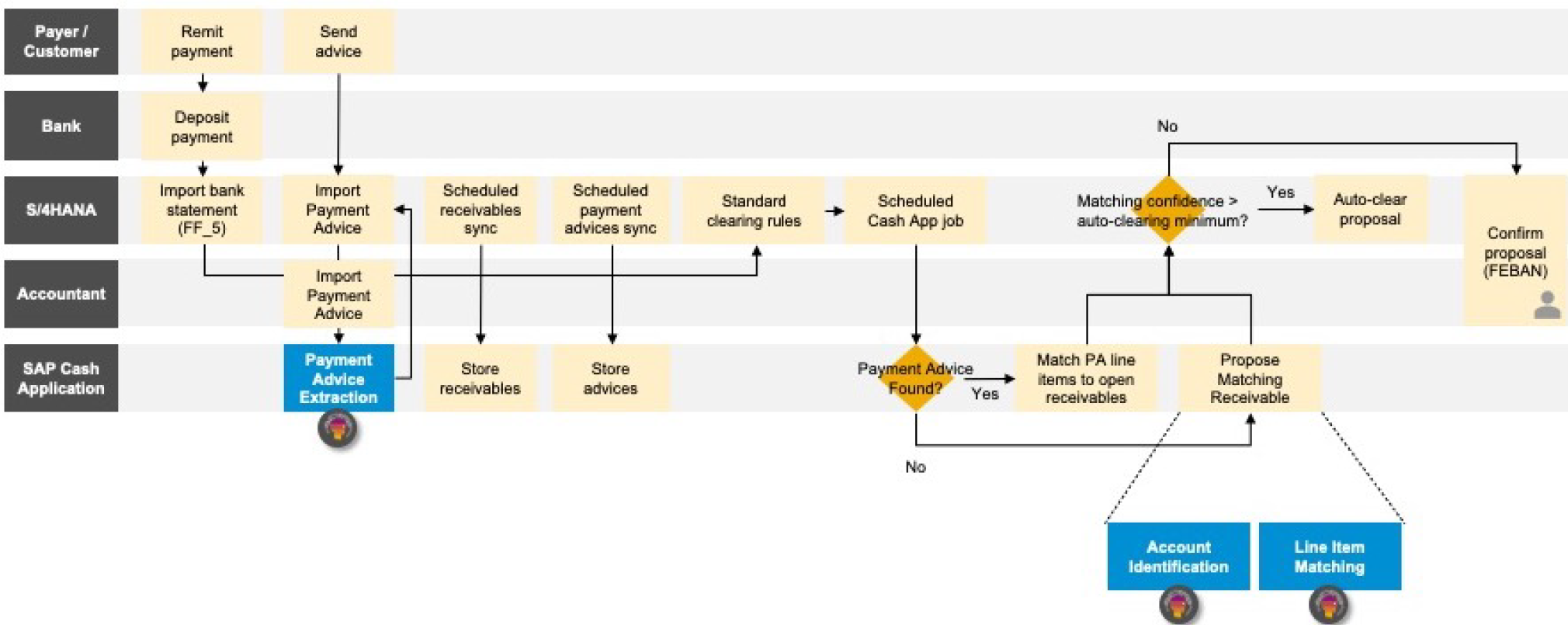
Figure 3: Payment Advice Extraction for SAP Cash Application allows unstructured data to be
incorporated into the A/R process.
Once the machine learning algorithm is applied, many exceptions to the open items can be cleared.
A company may choose to allow the application to post these cleared items automatically, as long as they meet the designated confidence level, such as 90% certainty that the logic applied has resulted in the correct proposal. This tolerance level can be configured in SAP Cash Application. Other companies may choose disallow automatic postings, choosing to examine the line items that would have been posted and then manually release them. Typically, after some time, most companies do allow the system to post these items automatically. This leaves only a fraction of the line items that must still be handled manually as true exceptions.
SAP Cash Application is built on SAP S/4HANA Finance, leveraging both the core A/R processes and the machine learning engine. It has been available in the public cloud since release 1802 and on premise since release 1709. A special adapter has now been built to allow the application to run against SAP ECC 6.0, with EHP7+.
Now that we understand the capabilities of SAP Cash Application as part of the overall A/R process, let’s take a look at how the machine learning engine is trained to create the appropriate algorithms.
Training the Machine Learning Engine
Before implementing SAP Cash Application, the machine learning engine must be trained to learn and incorporate knowledge of prior transactions and how exceptions were handled, even when handled manually. Figure 4 highlights the process of training the machine learning engine.
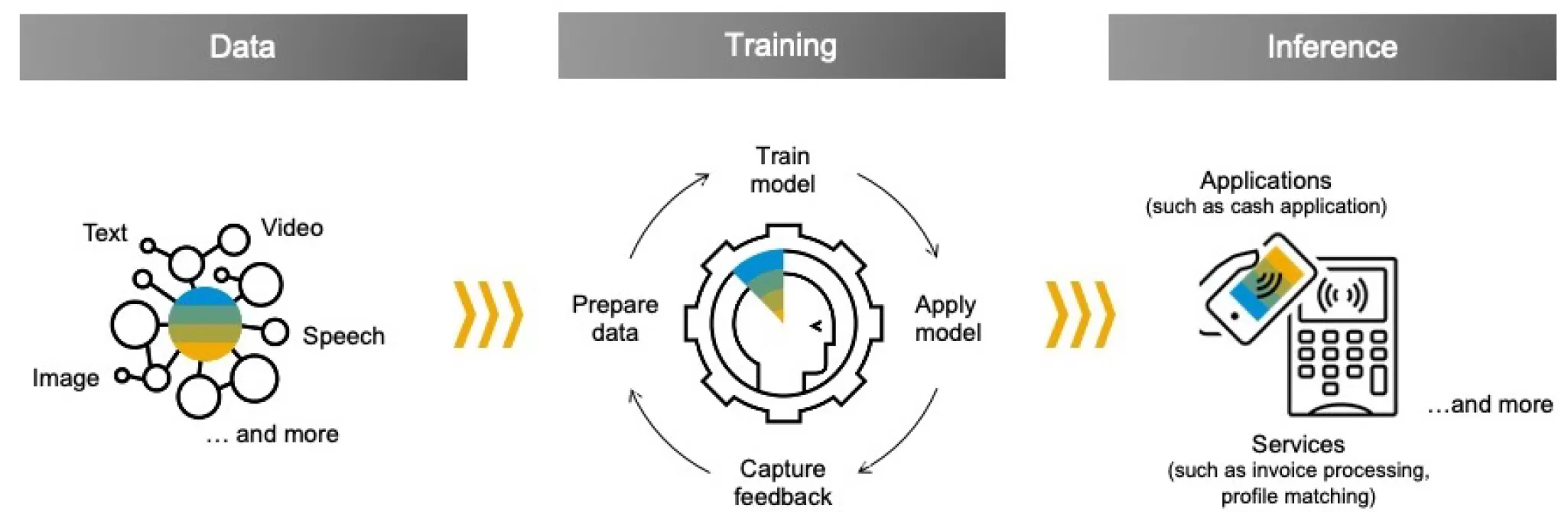
Figure 4: Training of the machine learning engine involves incorporating historical information,
iteratively processing this logic on new data sets and incorporating feedback to refine the algorithm to make the correct inferences on the receivables open items.
Training begins with the incorporation of historical information, which includes business partner information such as the customer ID and customer name, bank master data, and product master data. Additional transactional information includes prior electronic bank statements, notes and payment advice records, payer bank account information, and core financial accounting documents in the Universal Journal.
The machine learning engine builds an algorithm by learning the correct decision criteria, tolerance of values, and the priority of applying them against incoming payment transactions. Then, with the preliminary algorithm created by the machine learning engine, this logic is used iteratively on new data sets. The system again learns with feedback from the finance team on which recommendations are appropriate and which are not.
Once this iterative training cycle has been completed, the logic is used to infer the correct actions. For example, with no match of a business partner in an incoming record, the correct customer number can be inferred from bank statements by matching the reference number of a particular transaction. Once trained, it is not necessary to “re-train” the machine learning engine in the future. While new exceptions may result after a change in business processes or the business environment, the system learns how to handle these exceptions on an on-going basis and incorporates them to refine the algorithm used to match receivables where there are future similar exceptions.
SAP Cash Application has embedded the machine learning engine that is part of the SAP AI Core, which is delivered in the SAP Cloud Platform. The application, while residing in the cloud, can run against both on-premise and cloud implementations of SAP S/4HANA Finance.
Next, let’s take a look at how to verify that SAP Cash Application made the correct decision for
SAP Cash Application using Machine Learning Read More »